When it comes to snagging inspections, professional surveyors today rely on a blend of traditional and advanced tools to identify defects in new-build properties. These tools help catch both visible and hidden issues from poor workmanship to thermal inefficiencies ensuring new homeowners can hold developers accountable. In this 2025 guide, we’ll walk through the most important tools used in professional snagging inspections, why they matter, and how they improve the quality and reliability of snagging reports.
Why Tool Choice Matters in Snagging Inspections
A snagging inspection isn’t just about spotting obvious cosmetic issues like paint drips or misaligned doors. Professional snagging surveyors are looking for structural and latent defects that can lead to costly repairs or safety hazards later. The choice of tools directly influences:
- Accuracy: High-precision measurement tools ensure that dimensions, levelness, and alignment are within acceptable tolerances.
- Detection of hidden issues: Tools like thermal imagers and moisture meters reveal problems not visible to the naked eye, such as damp, heat loss, or electrical hot spots.
- Safety and access: Drones or telescopic cameras help inspect hard-to-reach areas like roofs or high facades safely.
- Efficiency: Digital tools and software streamline data collection, reporting, and follow-up, making the snagging process faster and more transparent.
Key Tools Used in Professional Snagging Inspections (2025)
Here are the top tools that professional snagging inspectors commonly use today, and how they enhance the inspection process:
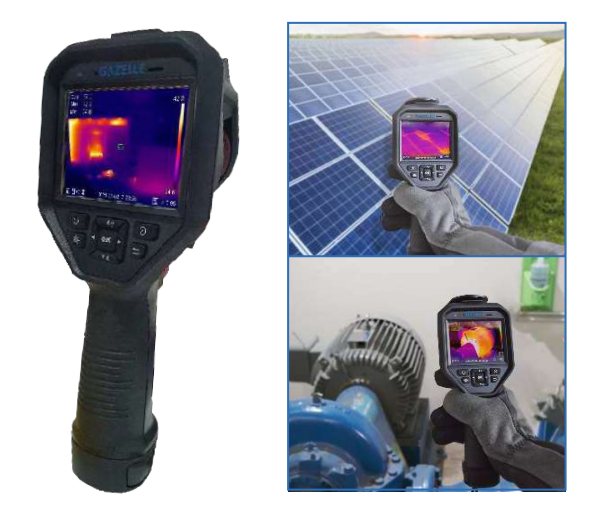
Thermal Imaging Cameras
One of the most powerful tools in a snagging inspector’s kit is a thermal imaging camera. These devices detect temperature variations on surfaces, which can signal underlying issues such as:
- Poor or missing insulation
- Moisture ingress or leaks
- Electrical hotspots or overheating wiring
Professional snagging companies routinely use thermal imaging during inspections to produce thermographic reports.
These insights are critical not just for aesthetics, but for long-term energy efficiency and safety.

Drones / Aerial Inspection Tools
Roof, gutter, and high-level facade inspections are challenging and sometimes dangerous to perform manually. Drones provide a safe, efficient way to survey these areas. Surveyors can capture high-resolution aerial images or video to:
- Identify roof tile defects, missing or loose elements
- Check guttering, downpipes, and flashing
- Inspect chimneys, dormer windows, or soffits
Snagging companies offer optional drone inspections as part of their survey packages.
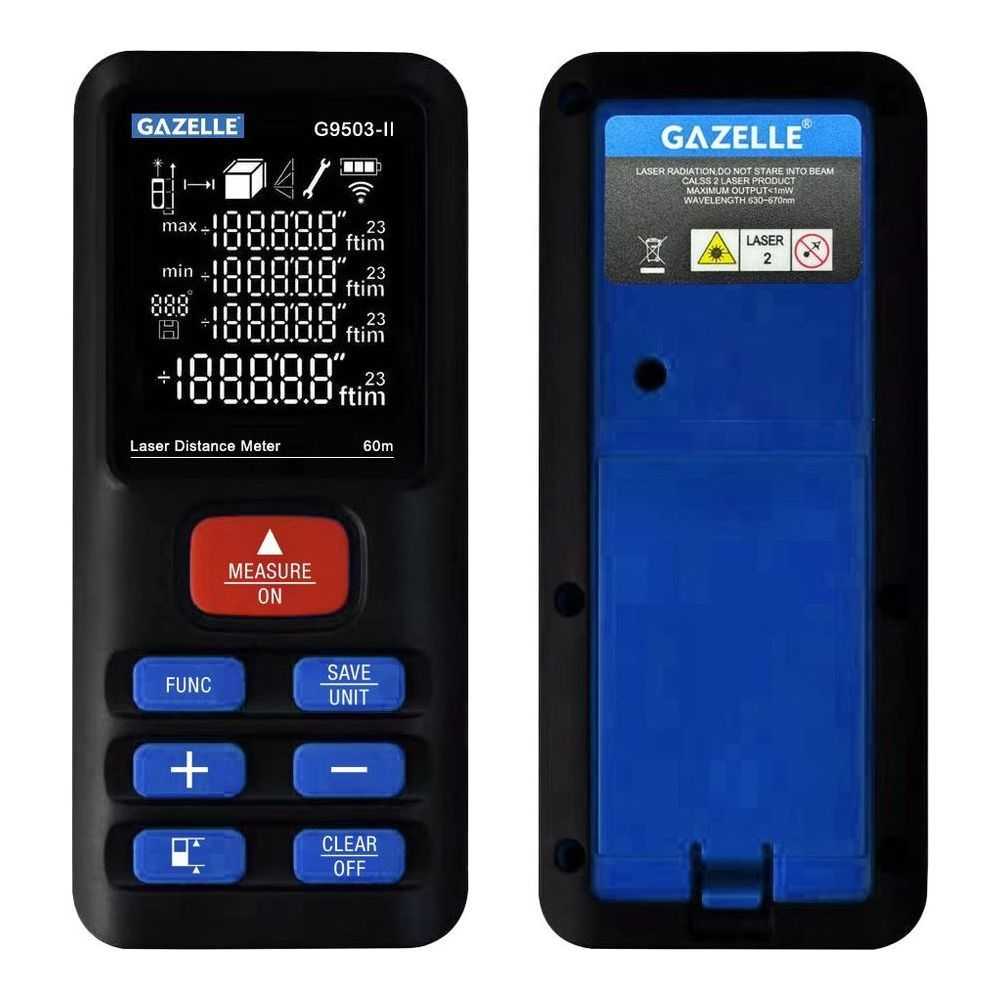
Laser Distance Meters
Accurate measurement is fundamental in snagging. Laser distance meters (or laser measures) are used to precisely measure room dimensions, ceiling heights, and the alignment of walls or openings. These devices help inspectors:
- Compare actual measurements with architectural plans
- Check whether surfaces are plumb, level, or square
- Identify uneven floors, walls, or misaligned fittings
Advanced laser measurement tools, sometimes combined with augmented-reality features, are increasingly common in modern snagging workflows.

Moisture / Damp Meters
Dampness is a silent but very common defect in new builds. A moisture meter is a specialized instrument that measures the moisture content in walls, floors, or ceilings. This helps:
- Detect water ingress or leakage behind plaster or drywall
- Highlight areas susceptible to mold growth
- Determine whether damp is active or residual
Surveyors always carry reliable electronic moisture meters, often with spare batteries, and calibrate them according to manufacturer instructions.

High-Resolution Digital Cameras and Photographic Equipment
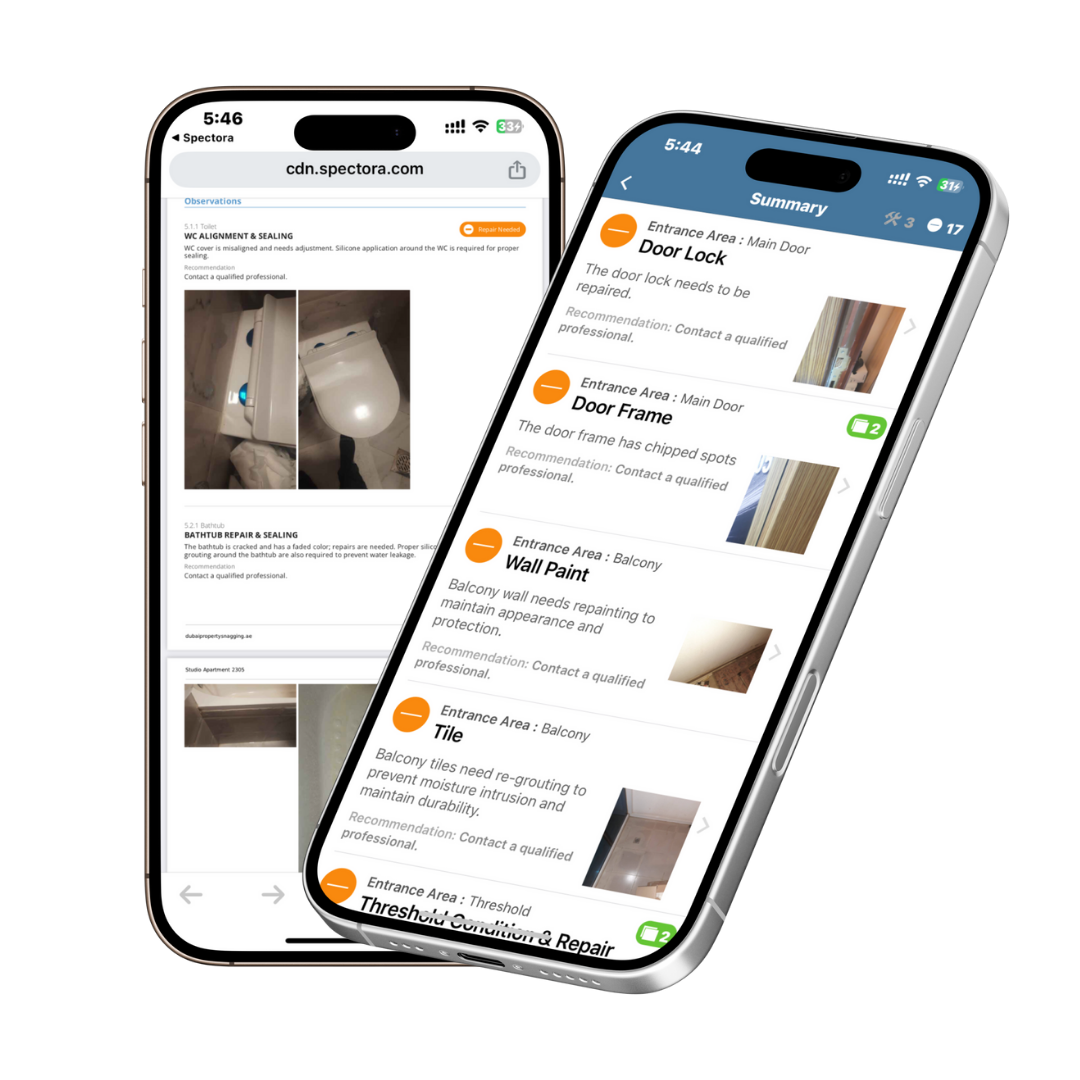
Visual documentation is critical. Professional inspectors use high-resolution cameras to photograph all defects. These images are essential for:
- Generating clear, professional snagging reports
- Providing evidence for builders to rectify issues
- Offering transparency and accountability to homeowners
Some snagging companies also include video evidence, links to guidance images, or even annotated photos in their reports.
Laser Levels or Digital Angle Levels / Spirit Levels
To check alignment and levelness of building elements, inspectors use spirit levels or digital angle levels. These help in:
- Assessing whether window sills, door frames, or skirting boards are level
- Measuring slope or deviation from plumb
- Ensuring that surfaces meet tolerance standards
The RICS equipment checklist recommends using either traditional spirit levels or digital devices.

Borescope / Endoscope
For inspecting tight, hidden spaces — such as within cavity walls, ducting, or floor voids — a borescope or endoscope is invaluable. These are flexible cameras on a cable that can be inserted into small openings to:
- Check insulation quality within wall cavities
- Inspect hidden structural joints
- Identify trapped moisture or poor workmanship
Some professional snaggers offer borescope checks of cavity walls as part of their detailed survey.

Binoculars
While it may seem basic, binoculars are still very useful for snagging inspections, especially for surveying high or distant areas such as rooflines, chimneys, or guttering. According to RICS’s standard equipment list, 10× binoculars help inspectors observe external features safely from the ground.
Magnet
A strong magnet may sound unusual, but it’s a useful tool for inspectors to detect certain metal components or to check for ferrous (iron-based) materials in structures. RICS guidance includes that magnet as part of the standard toolkit.
Plumb Bob
A plumb bob is a simple traditional tool used to verify vertical alignment (plumb) of walls or structural members. It remains relevant because of its reliability and simplicity — particularly in assessing verticality.
Pocket Mirror or Telescopic Search Mirror
Inspectors use small mirrors or telescopic mirrors to view under floorboards, inspect ductwork, or probe otherwise inaccessible cavities. This helps in spotting issues inside hidden zones safely.
Ladder and Safety Equipment
Physical access is often needed, so ladders (appropriate height, stable), plus protective clothing (hi-vis jackets, helmets, gloves, safety shoes), are essential. Inspectors should also bring tools like crow bars to lift inspection chamber covers safely.
Software & Mobile Inspection Apps
Modern snagging isn’t just about physical tools — digital tools are equally important. Surveyors use inspection apps (like specialized “snag list” apps) to:
- Record snags on-site with time-stamped notes
- Capture photos, video, and geolocations
- Generate professional, structured reports
- Track resolution of defects in collaboration with clients and builders
For instance, NestForms offers a punch-list app that gives surveyors real-time report capabilities. Many snagging companies also use proprietary apps to categorize snags into priorities (e.g., red/amber), attach supporting media, and export to PDF or Excel.
How These Tools Fit into the Snagging Process
- Pre-Inspection Setup: Surveyors calibrate moisture meters, check batteries on thermal cameras, and set up ladder & safety gear.
- Exterior Inspection: They use binoculars and drones to inspect roof, guttering, and external façade. Thermal scans may be done from outside.
- Interior Inspection: Inside, they measure with lasers, check levelness, use plumb bobs, and inspect cavities with borescopes.
- Hidden Defect Detection: Thermal imaging helps highlight moisture or insulation issues; moisture meters confirm damp levels.
- Documentation: App-based tools + high-res cameras capture every snag thoroughly. Notes, photos, videos are tagged and coded.
- Report Generation: Using digital forms, the app compiles a professional snag list report, often with a priority grading (e.g., red = critical, amber = cosmetic).
- Follow-up: Surveyors may schedule re-inspections to verify whether the builder has addressed the snags.
Benefits of Using Advanced Tools in Snagging
- Reduced Risk of Missed Defects: Hidden or latent issues that are invisible to an untrained eye are more likely to be detected.
- Improved Builder Accountability: Detailed snag reports backed by thermal imaging or drone photos make it harder for developers to dismiss or delay fixes.
- Faster Turnaround: Digital tools speed up data collection and report generation, so snagging surveys can be delivered quickly.
- Enhanced Safety: Using drones, mirrors, and telescopic tools reduces the need for unsafe or risky manual access.
- Better Client Communication: Professionally generated snag reports with images, videos, and structured data are easier for homeowners to understand and act on.
Challenges & Considerations
While these tools greatly enhance snagging inspections, surveyors must also address some challenges:
- Training & Competence: Advanced tools like thermal imagers and borescopes require specific training to be used effectively and interpreted correctly.
- Cost of Equipment: High-end inspection devices (drones, thermal cameras) are expensive, potentially increasing the cost of a snagging survey.
- False Positives / Data Interpretation: Thermal anomalies may not always indicate a real defect — they could be due to environmental factors, so professional interpretation is critical.
- Data Security: Digital records, photos, and reports must be stored securely, in compliance with data protection regulations.
- Regulation & Standards: Inspectors must adhere to industry standards (such as RICS) to ensure their methods are accepted by developers or warranty providers.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is a snagging inspection?
A snagging inspection is a detailed check carried out by a professional surveyor on a newly built or recently renovated property. The inspector identifies defects, unfinished work, or poor craftsmanship (called “snags”), and produces a report for the homeowner and builder.
Q2: When should you schedule a snagging inspection?
Ideally, a snagging inspection should be done either just before legal completion (pre-completion inspection) or shortly after move-in, while the developer’s warranty is still valid. Many snagging firms recommend having the inspection done within the first few months.
Q3: Do professional snagging inspectors always use drones?
Not always it depends on the surveyor’s service package and the property. Some snagging companies offer drone inspections as an optional extra.
Q4: Is thermal imaging essential for snagging inspections?
While not strictly mandatory, thermal imaging is very valuable. It helps reveal problems like insulation gaps, water ingress, and heat-loss that may not be visible otherwise. Many professional snagging firms include thermal imaging in their advanced surveys.
Q5: How does a borescope help in snagging?
A borescope (or endoscope) is a flexible camera that can be inserted into small openings, such as cavity walls, ducts, or floor voids. It allows inspectors to see hidden areas, check insulation, look for moisture, and assess the quality of internal finishes.
Q6: Are these inspections expensive?
The cost depends on the scope of the survey, the tools used (e.g., drone, thermal imaging), and the size of the property. Higher-end inspections with advanced technology tend to cost more, but the investment often pays off by uncovering defects early, potentially saving money in the long run.
Q7: Can I do snagging inspection myself?
You can perform a DIY snag list to catch obvious issues, but you won’t have the same insights as a professional surveyor equipped with specialized tools (thermal camera, borescope, etc.). Professionals can spot latent defects, provide a structured report, and help enforce fixes with the builder.
Q8: How reliable are digital snagging apps?
Very reliable, when used by trained inspectors. Apps help standardize data collection, attach multimedia evidence (photos/videos), and generate well-organized reports. They also improve accountability and reduce human error compared to manual, paper-based snag lists.
Conclusion
In 2025, snagging inspections are more thorough and technology-driven than ever. Professional surveyors are combining traditional tools like plumb bobs and binoculars with advanced equipment like drones, thermal cameras, and borescopes. This powerful toolkit allows them to deliver highly accurate and actionable snag lists, helping homeowners ensure that their new-build property meets quality standards.
If you’re buying a new property, investing in a professional snagging survey especially one that uses modern tools can give you peace of mind, document defects clearly, and help you enforce repairs before problems spiral.